• how do you start
I suggest to build it on the watersurface as craning a whole room with windows looks like a manouver that would in practice probably cost more than building the room itself.
Second it is expensive and complicated to get a building place on the waterfront of the required size in any marina and shipyard as the waterfront is the bottleneck of the whole operation.
The idea to have a room of hundreds of tons sitting there during months of building and then sourround it with heavy cranes that can lift and move it with beams large enough to reach out on the watersurface is nightmarish at least…especially if you pretend to keep up operations with fragile white shiny glasfiber yacht around it.
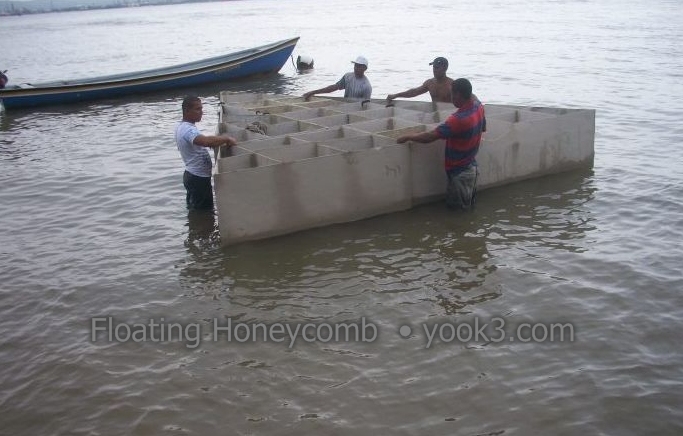
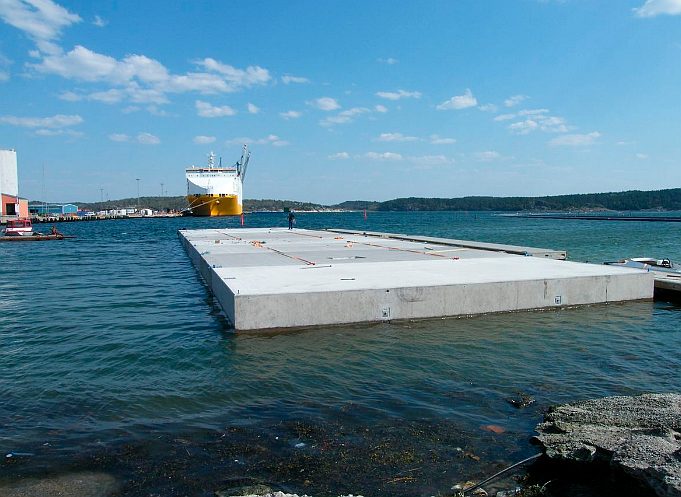
So it is best to build on the watersurface where you have plenty of space and do not interfere with other operations that need the high value waterfront. (context)
There is a good reason why oil platforms are no longer built on land - and then floated out…as you see it in the context images.
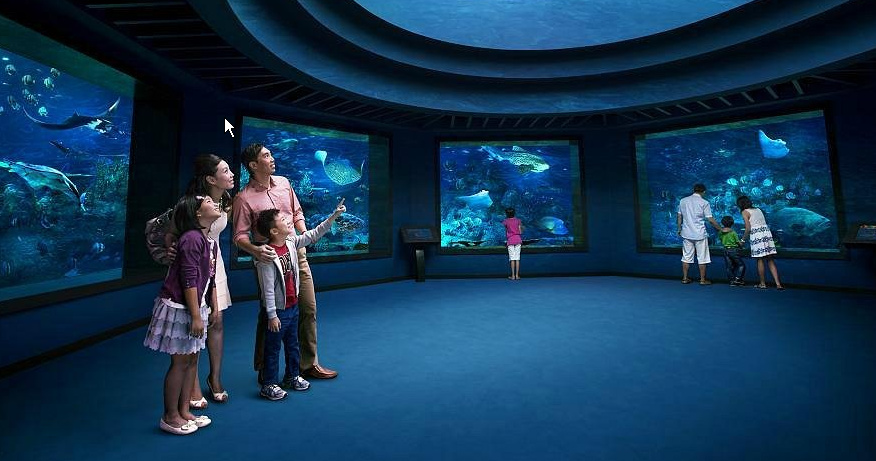
Lets take this image as a “frame paradigm” what we mean when talking about an underwater room"
Be aware that what the picture shows is a air volume of maybe 600 tons and above so to get it underwater you need a weight of 600 tons…that is not a thing you can move around on land or transition from land to water. Like a whale it must be born (built) in the water, while supported by water, and stay supported by water for all its lifetime.
So something that has a generous size and is clearly out of the range of craning and moving it around on land.
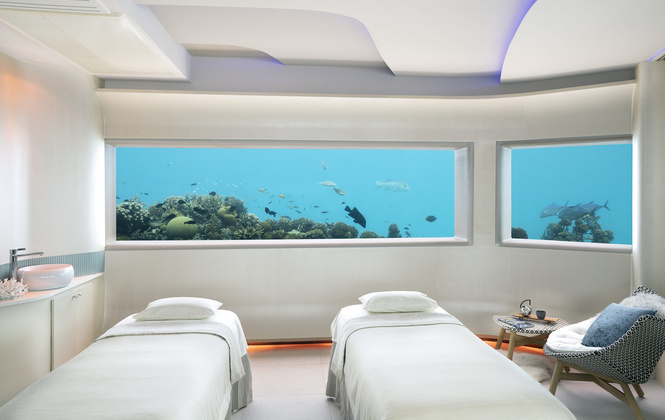
It also implies that it can not be “taken out of the water” like boats yachts and ships - not even in a big, specialized, and expensive, installation like a drydock
Therefore the acrylic windows that come to mind first, are not a very good option as they scratch easy, can be completly ruined with the wrong cleaning product, tend to age poorley.
There is a good reason why acrylic is NEVER used for windows in buildings like skyscrapers. It only looks good for a few months - not good enough for real estate where you want to “sell the view” for decades to come.
What you want to avoid is a situation where you have a room that you can not take out of the water but the windows have become ugly and you have no way to replace them.
So it is convenient to go for something that has a good durability record.
Imagine you send a diver down there to clean the windows - what you need to do every second day - and a small shell creature on the window gets squashed and leaves a mayor scratch clearly visibe, every single time you do the process.
So in practice you perfer laminated glass windows - what leaves you with the option of bus windows.
The building strategy is not designing the room and then custom fabricate the windows for it - it is better the other way round - get the windows - for example a dozend bus front windows and then build the room to provide a frame for those windows.
context : the case for bus windows
The room has 3 parts
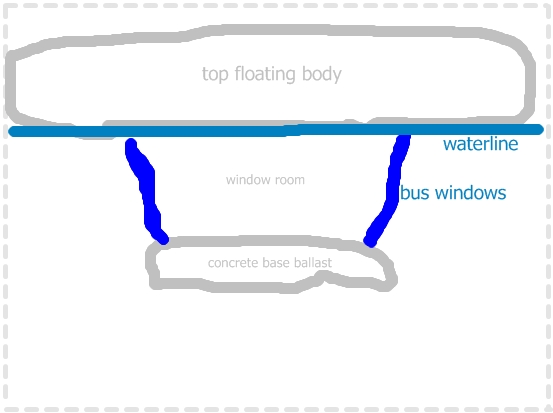
This 3 part strategy is the base to get something that is unsinkable even if one of the windows should break
Imagine the room is full of people and then it starts not only flooding quickly but simultaneysly sinking as the water pouring in adds to to the weight and eats up buoyancy.
The minimum you need is that the flooded room stays on the surface and people can escape to the top floating body easyly.

















